Bacterial and viral infections have many things in common. Both types of infections are caused by microbes -- bacteria and viruses, respectively
The Differences Between Bacteria and Viruses
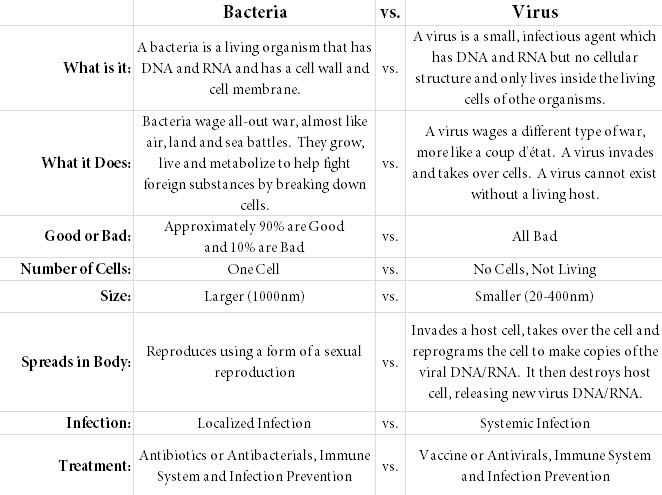
Although bacteria and viruses are both too small to be seen without a microscope, they're as different as giraffes and goldfish.
Most bacteria are harmless, and some actually help by digesting food, destroying disease-causing microbes, fighting cancer cells, and providing essential nutrients. Fewer than 1% of bacteria cause diseases in people.
Viruses are tinier: the largest of them are smaller than the smallest bacteria. All they have is a protein coat and a core of genetic material, either RNA or DNA. Unlike bacteria, viruses can't survive without a host. They can only reproduce by attaching themselves to cells. In most cases, they reprogram the cells to make new viruses until the cells burst and die. In other cases, they turn normal cells into malignant or cancerous cells.
Also unlike bacteria, most viruses do cause disease, and they're quite specific about the cells they attack. For example, certain viruses attack cells in the liver, respiratory system, or blood. In some cases, viruses target bacteria.
The Differences Between Bacteria and Viruses
Although bacteria and viruses are both too small to be seen without a microscope, they're as different as giraffes and goldfish.
Most bacteria are harmless, and some actually help by digesting food, destroying disease-causing microbes, fighting cancer cells, and providing essential nutrients. Fewer than 1% of bacteria cause diseases in people.
Viruses are tinier: the largest of them are smaller than the smallest bacteria. All they have is a protein coat and a core of genetic material, either RNA or DNA. Unlike bacteria, viruses can't survive without a host. They can only reproduce by attaching themselves to cells. In most cases, they reprogram the cells to make new viruses until the cells burst and die. In other cases, they turn normal cells into malignant or cancerous cells.
Also unlike bacteria, most viruses do cause disease, and they're quite specific about the cells they attack. For example, certain viruses attack cells in the liver, respiratory system, or blood. In some cases, viruses target bacteria.
Comments
Post a Comment